What Is Coproculture?
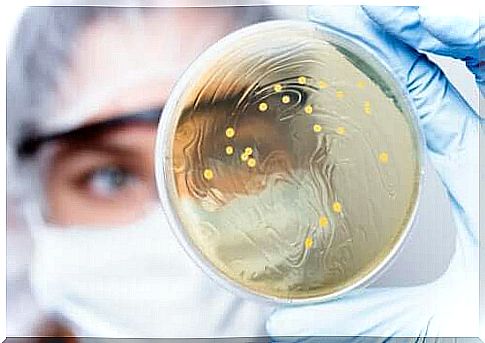
Stool culture, or stool culture, is an effective method for identifying pathologies of the digestive system associated with infections. This is a common mechanism for conducting various scientific studies to draw conclusions about the presence of bacteria and parasites in the intestine.
Frequently, parasites, viruses and bacteria infect us, generating various symptoms of intestinal discomfort. In addition, there are pathologies that manifest through bleeding in the stool, such as colitis, gastric cancer and stomach ulcers. For these and other cases, a stool culture is an essential test of detection.
About microbiological cultures
Microbiological culture is a method based on the multiplication of microorganisms in a sterile medium, usually bacteria, to facilitate the detection of a disease-causing pathogen. In short, it consists of providing these pathogens with the ideal environment for their development.
The sowing of biological samples from patients comes from sputum, saliva, parts of the skin or feces. These samples are placed in small containers called Petri dishes , with a solid substance containing agar.
Many pathogens have specific growth requirements, therefore, each culture medium is specialized based on the microorganism under investigation, as reported by this specialized immunology portal. Some of these parameters are as follows:
- Availability of nutrients suitable for bacterial growth.
- Presence or absence of oxygen and other gases.
- Adequate humidity conditions.
- Ambient light.
- Acidity or alkalinity.
- Temperature.
- Environmental sterility.
Depending on the types of microorganisms investigated, the conditions in the culture media must be different. Once observed its growth on the plate, samples are isolated and will be observed through the microscope, to identify the specific species causing the disease.
As many scientific sources point out, there are many different types of staining techniques for identifying bacteria. In these techniques, dyes are used that dye the microorganisms, thus facilitating their detection. The most common for medical use is the Gram- type stain .
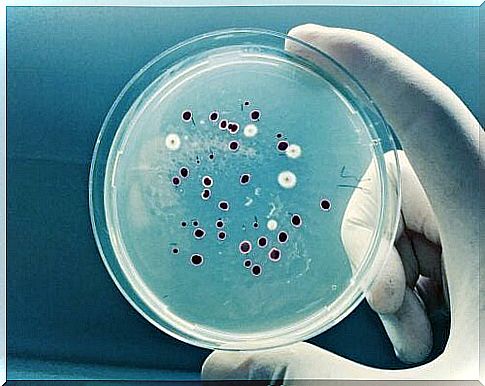
To learn more: 9 dangerous bacteria most harmful to humans
What is a stool culture?
According to what we have been commenting, stool culture is nothing more than a microbiological culture based on the collection of feces as a sample from the sick patient. This test is used, above all, to study cases of persistent or recurrent diarrhea for no known reason.
As stated in this medical review article, collection of faecal samples is necessary in enteric infectious conditions that do not resolve within two to three days.
Some of the pathogenic microorganisms that are identified by stool culture are: Salmonella, Campylobacter, Helicobacter, Shigella, Yersinia, Clostridium difficile and Staphylococcus aureus .
Sample collection
The review article we cited indicates the steps to be followed to collect the sample for stool culture:
- The patient’s stool should be collected in an airtight container with a wide mouth, with a minimum sample volume of two to four grams in soft stools and five to ten milliliters in liquid stools.
- Faecal samples that have been exposed to the environment for two hours or more, or are contaminated with urine or toilet paper scraps, are not valid.
- A very small sample is taken from the patient’s stool and seeded in a culture medium suitable for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
- If the professional does not detect the presence of enteropathogens with the first sample, then it will be necessary to collect two more portions on different days.
- Once the pathogenic bacteria are identified, the appropriate antibiotic is prescribed.
What is observed in a coproculture?
These microbiological cultures are used for the classification of various pathologies through the identification of bacteria, seeding of the fecal sample and its subsequent coloration. Possible eggs or remains of parasites are also examined.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) , it is possible to identify parasites such as tapeworms in fecal cultures, since it is possible to observe their eggs in the patient’s feces. Likewise, if there is occult blood that is not seen at first glance in the stool, the biochemist can detect it by culturing the stool.
Constraints of coproculture
Not everything is ideal in the world of microbiological cultures. It is not always possible to achieve the results, and these depend, to a great extent, on the quality with which the sample is obtained. As this scientific article states, there are certain risks when it comes to identifying diseases through stool culture.
First, biochemists do not routinely screen for all enteropathogens. As the culture medium is specific for the microorganisms that it intends to find, some less common ones, such as Bacteroides fragilis, Edwarsiella takes or Escherichia alberti , may not grow.
Furthermore, there are pathogens that are not yet known and for which specific biological requirements will be needed. Therefore, as there are no suitable conditions available, it is possible that they will not multiply on the plate. It is something that escapes the specific clinical situation, in which the intention is to research the most common diseases.
Other studies argue that coprocultures are inadequate in people hospitalized for more than three days. This is because the cause of diarrhea is not attributable to pathogens in the gut. In these cases, the PCR detection technique is chosen, identifying specific genes of a microorganism in the fecal sample.
Be sure to read: Natural treatments to fight Helicobacter Pylori
Coproculture: what to take into account?
These microbiological cultures are useful in identifying pathogenic enteric bacteria, parasites, and blood in the stool. Even so, due to the high cost and delay of the procedure, only those patients who justify it due to their epidemiological situation are selected.
In any case, if during a hospital stay they suggest a stool culture, there is no need to worry. Doctors are trying to pinpoint the exact pathogen responsible for the gastrointestinal disease so they can administer the most appropriate medication.