What Is Mupirocin?

Mupirocin is an antibiotic used to treat the vast majority of bacteria that give rise to skin infections.
How does mupirocin work?
This drug exerts its effect on the prevention of bacterial protein synthesis, through the inhibition of the enzyme isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase.
Due to its mechanism of action and chemical structure, it does not cross-resist with other antibiotics. The mupirocin is bacteriostatic at minimum inhibitory concentrations and bactericidal at higher concentrations reached when applied locally.
What is mupirocin indicated for?
This drug is indicated for the treatment of skin infections caused by sensitive microorganisms. Therefore, it is indicated for the treatment of primary skin infections, such as folliculitis, impetigo or forunculosis.
In addition, it is also prescribed when secondary dermatological infections, such as superinfected contact dermatitis, infected wounds, atopic dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis, appear, provided they are to a limited extent.
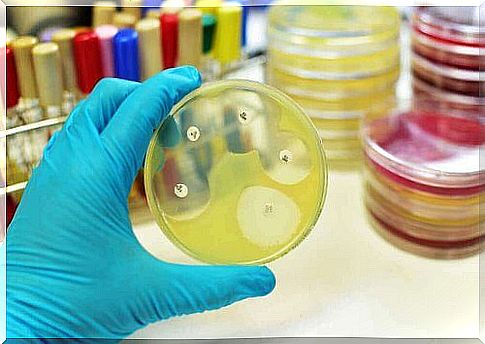
Mupirocin is a topical antibacterial agent that shows in vivo activity against Staphylococcus aureus , S. epidermidis and ß-hemolytic Streptococcus species .
However, in vitro , the spectrum of its activity includes bacteria such as :
- Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis .
- Species of Streptococcus.
- Haemophilus influenzae .
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis.
- Moraxella catarrhalis .
- Pasteurella multocida .
If your doctor has prescribed mupirocin to treat a cracked nipple, it is necessary to wash your nipple thoroughly before breastfeeding your baby.
How is mupirocin used?
In the case of skin problems, this antibiotic is presented in the form of an ointment. One application of mupirocin is given 2-3 times a day for 5 to 10 days, depending on the response. If after 3-5 days of treatment no improvement is seen, the diagnosis and/or treatment should be reconsidered.
It is first necessary to wash and dry the area to be treated. Afterwards, apply a small amount of the ointment and, if necessary, you can cover the area with a bandage or occlusive gauze.
It should not be mixed with other ointments as there is a risk of dilution. This would result in a decrease in antibacterial activity and, consequently, in a possible loss of stability of mupirocin in the ointment.
Adverse reactions and contraindications
The reported adverse reactions that mupirocin may cause were determined based on safety data. These data were collected from a clinical trial population of 1573 treated patients spanning 12 clinical studies.
At the level of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, localized burning may occur in the application area. Less commonly, itching, erythema, and itching may occur. Allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, generalized rash, urticaria and angioedema have also been reported.
On the other hand, the use of mupirocin is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to this active substance and to other components that appear in the formulation of ointments.
If you are pregnant or think you are, due to lack of information, you should not use mupirocin. Also, if you are breastfeeding, it should not be used as it can pass into milk and affect the baby.
What do you need to take into account?
In case of a sensitization reaction or strong local irritation when using this medicine, you must stop the treatment and remove the applied product. As an antibiotic with antibacterial action, its prolonged use can cause a proliferation of non-susceptible organisms.
Patients are unlikely to experience diarrhea during treatment with mupirocin as it is administered topically. However, if the patient experiences prolonged or significant dysentery or abdominal cramps, treatment should be stopped and a physician should be consulted.
Some mupirocin ointments also contain another substance that is macrogol. For this reason, ointments with this formulation should not be used when there is evidence of renal failure.
Macrogol can be absorbed through the damaged skin and later eliminated by the kidneys.
Care must be taken not to use mupirocin on very large areas of the skin. In the event of an overdose, there is no specific treatment, although if it does occur, the patient should receive supportive care and remain in control.
Conclusion
Mupirocin is indicated for the treatment of skin infections caused by sensitive microorganisms. However, it is important that the recommendations given in the package insert regarding proper use are taken into account.